What is it?
A CT coronary angiogram is a diagnostic imaging test that involves creating images of the heart, blood vessels and tissues to identify issues or discrepancies if any. It involves the usage of a safe dye, which is injected into the blood so as to make the heart, blood vessels and tissues appear clearer in the images/scans.
Unlike a cardiac CT scan or a traditional angiogram, a CT coronary angiogram makes use of dye, injected intravenously, after which x-rays are used to create images of the organ and organ system.
How is it done?
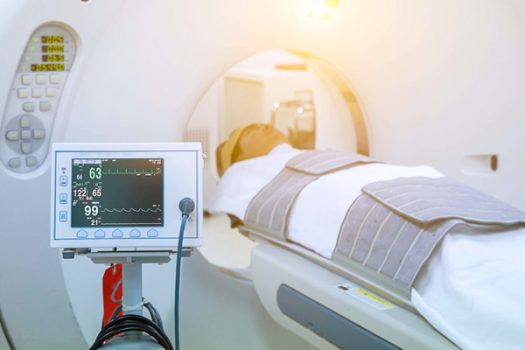
A CT coronary angiogram involves the patient taking a sedative medication, after which the dye is injected intravenously through the hand/arm. Once this step is complete, the patient will need to lie on the CT machine table, and the CT scans will be developed. The patient may, sometimes, be hooked up to several electrodes on the chest, which will develop ECG readings simultaneously.
In order to prepare for a CT coronary angiogram, you will have to follow the preparation steps instructed by the doctor. Once the procedure is complete, you can return to your daily routine, unless stated otherwise. You will be advised to stay hydrated, so as to flush the dye out of your system. Once your readings and scans are analyzed, you will be called in to discuss your heart’s health and issues, if any.
Why is it done?
A CT coronary angiogram can help doctors detect various heart-related issues, including:
- Aneurysms
- Atherosclerosis (fatty buildup in blood vessels)
- Coronary artery disease
- Pulmonary embolism